Россия
Россия
Разработка системы управления рыбопромысловым оборудованием, оптимальная компоновка промысловых светильников современными кварцево-галогенными и светодиодными лампами, использование орудий лова высокой механизации, применение электронных регулирующих устройств позволяют значительно повысить эффективность вылова рыбных объектов, реагирующих на свет надводных и подводных источников. Усовершенствование технологий по управлению качеством светового излучения и проектирование мощных автоматизированных систем поиска и лова рыбы должны вестись с учетом их влияния на общую судовую электроэнергетическую систему и требований, предъявляемых к ней. При исследовании системы автоматического регулирования напряжения светотехнической нагрузки, подключенной к синхронному генератору через тиристорный регулятор, необходимо учитывать множество факторов, ограничивающих применение других регулирующих устройств, такие как необходимость источника длительно выдерживать несимметричную нагрузку с разницей между фазными токами не более 20 % от номинального значения; широкий диапазон изменения напряжений; допустимое значение тока нулевого провода при применении четырехпроводной «звезды» должно быть не более 125 % от номинального фазного тока судового генератора и ограничено двумя часами длительной работы; полное использование (загрузка) генератора по мощности; минимизация массо-габаритных показателей всех устройств; поддержание на должном уровне показателей качества судовой электроэнергии и др. Учет всех этих факторов требует моделирования всей рассматриваемой системы в современных программных комплексах, которые позволяют определить временные диаграммы токов и напряжений моделируемой схемы, интегральные вычисления важных параметров и провести гармонический анализ. Исследованы способы ограничения тока нулевого провода и уменьшения вредного влияния его гармоник при применении тиристорных регуляторов напряжения для управления современными промысловыми светильниками на российских траулерах (в качестве источника для питания рыбопромыслового светотехнического оборудования рассмотрен судовой валогенератор МС-375-1000 с номинальным напряжением 400 В). Показано уменьшение уровней высших гармоник в судовой сети путем отделения нелинейных нагрузок, связанных с работой регулятора, с помощью резонансных фильтров.
регулирование светового потока, регулировочные характеристики, тиристорный трехфазный регулятор, светотехническое промысловое оборудование, ток нулевого провода синхронного генератора, фильтры
Introduction
Prospects for the development of fisheries for fish and aquatic organisms that respond positively to light (saury, squid, Black Sea and Pacific horse mackerel, Caspian sprat, anchovy, etc.) are associated with the use of various light sources, including modern energy-efficient LED lamps that have lower energy consumption and improved properties. Managing fish behavior in the fishery requires regulating lighting over a wide range by: changing the voltage supplied to the lamps, the number and arrangement of chandeliers with different radiation spectra, wavelengths and other parameters. Far Eastern scientists from the Pacific Research Fisheries Center of the Federal Agency for Fisheries (FGBNU TINRO-Center) propose original methods for improving lighting equipment and fishing devices used on large-tonnage and high-sided trawlers of the domestic fleet, which can significantly increase fishing productivity. These include on-board asymmetric traps (patent No. 2554979), used for stern pickup and new designs of high-intensity chandeliers [1]. Numerous studies and experiments have shown that the maximum positive effect is achieved by using well-proven lamps such as KGP (quartz-halogen lamps) and modern LED lamps (powerful LED spotlights, chandeliers) with smooth and step-by-step regulation of the luminous flux as fishing lamps [2-4]. The use of LED lamps also allows improving other types of fishing, including the extraction of various aquatic organisms (Pacific squid, flounder, etc.) using underwater lighting. The most important aspect for a stable catch and increased profitability is the ability to control the luminous flux and various spectrums of lamps of different types, combining the order of their connection and their power, which is implemented by special power and electronic equipment.
Research objects and methods
The research object is the power equipment of a large-tonnage trawler, a device for regulating the luminous flux and lighting equipment for fishing. The definition of the main characteristics of the regulator and the influence of the lighting equipment control process on the ship's electric power system were studied by means of computer modeling.
Results and their discussion
Fig. 1 a shows a simplified diagram of the arrangement of lighting equipment of a modern trawler: 1 – high-intensity LED lamps of red and white color with a power of up to 5 kW (placed at the lower level to concentrate the shoal under the working side); 2 – stevne chandeliers; 3 – extended high-power chandeliers (up to 18 kW) along the attracting side; 4 – upper chandeliers, placed above the deck at the height of the upper tier of the vessel's masts (for example, type KGP 200-5 000); 5 – indicators of maximum possible voltage; 6, 7 – fishing gear (lower and upper pick-ups), there is also other additional lighting in the form of special lamps and powerful commercial LED spotlights.

а b
Fig. 1. Lighting equipment of a fishing vessel: a – layout of fishing lighting;
b – external view of a sayrolov at a fishing site
Each type of chandeliers is placed at a certain angle, determined experimentally. Fish behavior is controlled by manipulating the light flux by regulating the voltage (voltage regulator control panel) and alternately switching on and off different groups of chandeliers (switch), as well as moving the vessel closer to the fishing gear with steering devices [1, 5].
Fishing lighting equipment must be able to regulate the luminous flux over a wide range of voltages from 30 to 110 percent of the nominal voltage of the lamps (U = 220 V). The total power of all chandeliers, lamps and spotlights is at least 300 kW, and in the future, when building large trawlers with combined fishing equipment for underwater nd surface lighting, up to
1 000 kW.
For these purposes, three-phase thyristor voltage regulators are used on modern vessels, which are connected with the terminals of a separately allocated synchronous shaft generator (so as not to overload the ship's power plant) and groups of fishing lamps distributed over three phases (Fig. 2, where A, B, C – wire line; N-n – neutral wire line; RA, RB, RC – active resistances in load phases; VT1-VT6 – thyristors; eA, eB, eC – electric movingpower of generator; ZA, ZB, ZC – resistance of generator and lines; ZN – resistance in neutral wire line; TK – thyristor keys; Ra, Rb, Rc – resistance of load; Zf – resistance of resonance filters in filter compensating device).

а b
Fig. 2. Power supply system of the SG and fish-finding light sources:
a – three-phase symmetrical thyristor voltage regulator; b – equivalent circuit for calculating the parameters
A shaft generator is the main problem that arises when power equipment, is operating on fishing lighting equipment is the uneven distribution of the load due to the need to regulate the luminous flux from different sides (connecting chandeliers). Since the control of the lamps is carried out by switching on and off individual groups connected to different phases, the voltage on the phases will be different, and the greater the difference in asymmetry, the greater the current flows through the neutral wire.
To use the maximum generator load in terms of power and to eliminate the inevitability of phase voltage asymmetry when controlling the light flux, it is necessary to use a four-wire “star” circuit with the connection of neutral points of the load and the generator, while the voltage drop in the neutral wire will be insignificant due to the low value of its impedance.
During long-term operation, asymmetry of phase currents up to 20% of the nominal is allowed. But since the operation of power equipment when regulating light at a fishing site is considered to be relatively short-term according to the Rules of the Maritime Register, the permissible value of this current is 125% of the nominal phase current of the generator for 2 hours. In this case, the extreme case of asymmetry must be excluded, when any of the phases is disconnected (disconnection of a group of chandeliers) with the nominal load of the other two phases, the current in the neutral wire becomes equal to the nominal phase current (the so-called phase break).
In any case, in the process of controlling the luminous flux (changing the number and power of the chandeliers in the phases) the current of the neutral wire of the generator must be maintained at a level of no more than a third of the nominal phase current. Since the chandeliers are made single-phase, it is necessary to observe the order of their connection in such way that the number of chandeliers connected in different phases should not differ by more than one (the maximum power of one LED chandelier can be taken as 10 kW on average, and for KGP type lamps – 12 kW).
To study the influence of the technological process of fishing on light and the features of the operation of power equipment when regulating the luminous flux in the required voltage range of commercial lamps, a four-wire power supply system was modeled, shown in Fig. 2, including a synchronous Sairol generator (technical characteristics of marine power equipment of domestic vessels of the STR-420 type are used) and a thyristor AC voltage regulator operating on a three-phase active-inductive load connected according to the “star” scheme.
The determination of the main parameters: voltages on industrial lamps, еxisting values of currents, as well as the installed powers of the filter elements was carried out by modeling on a PC of processes in the equivalent circuit of the electrical circuit under consideration for
a range of thyristor control angles from 0 to 180º.
In a thyristor regulator, the main elements are counter-parallel connected thyristors (thyristor keys TK Fig. 2, b) in each phase (the structural diagram is shown in Fig. 2, a). Such a diagram provides a wide range of voltage regulation of fishing light sources from 1.1 U nom at a control angle to zero at according to the following formula [6, 7]:
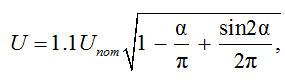
where α – thyristor control angle; U – relative existing value of load voltage (effective load voltage); Unom –nominal phase voltage of the load.
The relative effective value of the voltage on the chandeliers is conveniently considered in relation to the effective value of Umax / (at α = 0 it reaches 1.1).
When expanding this function in a Fourier series, the dependencies еxisting zero wire current value at α angle reduced to the еxisting value of the phase current are determined and analyzed.
Harmonic analysis of currents was carried out by modeling in the Matlab software package (Simulink, SimPowerSystems, etc.) via the Powergui functional block of the FFT Analysis Tool function, with the help of which it is possible to obtain the harmonic spectrum of the sought parameters in the form of a Fourier series (in Fig. 3: curve 3 is the third harmonic, curve 4 is the ninth; curve 5 is the remaining harmonics, except for the fundamental third).

Fig. 3. Dependence of the current values on the control angle [7]:
1, 2 – effective values I of the phase and neutral wires;
3-5 – harmonics of the generator neutral wire current
The harmonic analysis showed that the current of the generator neutral wire is greater than the currents of individual harmonics (the dependencies are shown in fractions of the effective value I0 of the phase current). This factor determines the need for its limitation.
Filter-compensating devices (three-phase low-pass filters) are the main methods for reducing harmonics contained in the neutral wire current. However, the study revealed that the total power of the filter elements for the system under consideration was unacceptably large in terms of weight and size indicators. Therefore, another option was considered, namely: increasing the resistance of the neutral wire by using blocking active filters included in the neutral wire.
The criterion for selecting the optimal filter, in addition to the main function – limiting the current of the SG neutral wire – is the total installed power of each element, which determines the minimum weight and dimensions of the device.
When considering various filter options (two-terminal circuits consisting of a single reactor and various options for series-parallel connection of a capacitor and reactor) using computer modeling, it was found that the best in terms of weight and size and limitation of current IN, is a series resonant circuit and a single reactor [6]. Fig. 4 shows the control characteristics, constructed based on the results of modeling, of the considered control system for the luminous flux of combined fishery lighting with a single reactor included in the neutral wire between the neutral points of the load and the generator.

Fig. 4. Adjustment characteristics and dependences of current values on the control angle:
1, 2 – еxisting values of phase current and zero wire current value;
3, 4 – currents of the neutral wire of the generator with a reactor and without a filter
The graphs are plotted in relative units to the basic existing value of load voltage and currents: curve 1 is the control characteristic of the voltage regulator in a four-wire system with tightly connected neutral points of the generator and load; curve 2 – with a two-terminal network in the form of a reactor in the neutral wire (in the circuit according to Fig. 2), curves 3 and 4 are the currents in the neutral wire in these systems, respectively.
The results of the studies showed that a filter in the form of a single reactor, installed in the neutral wire between neutral points N and n in the circuit in Fig. 2 (the filter is not shown in the circuit), significantly reduces the еxisting values of zero wire current value.
The control characteristics and the graph of the change in current IN, are presented in comparison with the circuit without a reactor, i. e. with tightly connected neutral points. The results of computer modeling showed a significant reduction due to the additionally increased resistance of the neutral wire. The purpose of the modeling was to determine the best ratio of elements, i. e. the reactor inductance and the capacitor capacity, corresponding to the above criteria, which are easy to determine from the existing value of load voltage and power on these elements.
In the first case, when switching on a series resonant circuit with parameters L = 256 mH, C = 5 700 μF (inductance and capacitance of resonance filter), the maximum value of the neutral wire current was no more than 10% of the nominal current of the shaft generator at a = 90º (when four chandeliers are switched on in two phases, and five in the third). In this case, the total calculated power of the two-terminal network is approximately 5% of the source power. A similar effect is created by a single reactor without a magnetic core, which can be made of several coils connected in series or in parallel, which makes it possible to smoothly control the inductance and resistance by moving the distance between the coils, i. e. make the necessary settings. The total installed power of this reactor is less than 2% of the source power (QS = 0.015SS), and it allows limiting the neutral wire current to 30% of the nominal value. The advantage of the reactor is the absence of
a capacitor and convenient adjustment of its total inductance due to a special design. When designing automated control systems, it should be taken into account that industrial lamps and other ship LED devices are nonlinear elements, therefore, in developments it is necessary to take into account the compatibility of their operation with the ship's electric power system,
i. e. to use filter compensating devices to suppress currents of higher harmonics in the entire system, which will improve the required quality of electricity and the reliability of power equipment [9].
Conclusions
1. The paper considers the regulation of the luminous flux of halogen and LED chandeliers using a thyristor regulator, which allows automatic control of sufficiently powerful lighting fishing electrical equip
ment without excessive load on the ship's power plant.
2. It is shown that when using a semiconductor voltage regulator in a four-wire ship's power supply system, it is possible to reduce the asymmetry of phase voltages under different loads due to the combinatorial connection of search chandeliers to different phases. The control characteristics of the regulator and currents of the system under study are constructed.
3. It is established that when supplying a three-phase active load through a thyristor voltage regulator, it is necessary to limit the neutral wire current using rejection reactive filters.
4. Computer modeling showed the advantage of the reactor for practical use, consisting in the absence of a capacitor and convenient adjustment of its total inductance due to a special design.
1. Пат. 2554979 С1 Рос. Федерация, МПК A01K75/02. Устройства для промыслового освещения / Еремин Ю. В., Балло А. В., Мизюркин М. А., Кручинин О. Н.; № 2013152656/13; заявл. 28.11.13; опубл. 10.07.15.
2. Мизюркин М. А., Жук А. П., Кручинин О. Н., Волотов В. М., Еремин Ю. В., Ваккер Н. Л., Захаров Е. А. Анализ сайровой путины 2017 года и предложения по оснащению судов современными источниками света // Рыбное хозяйство. 2018. № 1. С. 95–100.
3. Баринов В. В., Осипов Е. В. Обоснование применения светодиодных люстр с разным спектром света для промысла сайры // Науч. тр. Дальрыбвтуза. 2024. Т. 70. № 4. С. 94–104.
4. Мизюркин М. А., Жук А. П., Кручинин О. Н., Еремин Ю. В., Буслов А. В., Волотов В. М., Ваккер Н. Л., Филатов В. Н., Захаров Е. А., Сытов А. М. Результативность промысла сайры судами, оснащенными различными источниками света // Рыбное хозяйство. 2019. № 1. С. 30–34.
5. Веккер Н. Л. Обоснование технологии совместного применения ламп накаливания и светодиодных источников света на промысле сайры: дис. … канд. техн. наук. Калининград, 2022. 113 с.
6. Матафонова Е. П., Бурханов С. Б. Особенности применения тиристорных регуляторов для управления световым потоком в промышленном рыболовстве // Energy Systems Environmental Impacts (ESEI 2021) E3S Web Conferences. 2021. V. 320. Art. 01015. P. 8. URL: https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202132001015 (дата обращения: 02.02.2025).
7. Матафонова Е. П. Регулирование напряжения рыбопромыслового светотехнического электрооборудования: автореф. дис. ... канд. техн. наук. Владивосток, 2001. 20 с.
8. Климаш В. С. Регулировочные свойства, энергетические показатели и моделирование в среде Matlab выпрямителей и регуляторов переменного напряжения: учеб. пособие. Комсомольск-на-Амуре: Изд-во КнАГТУ, 2015. 114 с.
9. Пат. 158871 Рос. Федерация, МПК Н02J 3/01. Фильтрокомпенсирующее устройство для трехфазных систем электроснабжения с нелинейными нагрузками / Белей В. Ф., Харитонов М. С.; № 2015117043/07; заявл. 05.05.2015; опубл. 20.01.2016; бюл. 2.